
Discover the critical role of metrological traceability in manufacturing and how it ensures precision, reliability, and quality in production processes.
Want to see it yourself? Join DCS, ZeroTouch, and Metrologic Group at the Quality Show this week in Nashville, TN! There, you can see QDMWEB QI, the Quality Intelligence Platform, in action with direct connections to Metrologic software and hardware and ZeroTouch contactless inspection. Just Click Here to let us know you'll be there and we can schedule a private session.
Metrological traceability is a cornerstone of precision in manufacturing. It ensures that measurements are consistent and reliable, which is crucial for maintaining the quality and safety of products. By linking measurements to national or international standards, manufacturers can guarantee that their processes are accurate and their products meet stringent quality requirements.

Without metrological traceability, it would be impossible to compare data across different machines, production lines, or even plants. This traceability allows for a seamless flow of information, enabling quick decision-making and problem-solving, which is vital for maintaining competitive advantage in the manufacturing industry.
A metrologically traceable system comprises several key components, including reference standards, calibration procedures, documentation, and a quality management system to keep it all organized. Reference standards are the benchmarks against which equipment is calibrated to ensure accuracy. These standards must be maintained and updated regularly to reflect the latest in measurement science.

Calibration procedures are the methods used to compare the accuracy of measuring instruments against the reference standards. This process must be meticulously documented to create a clear traceability chain. Documentation is essential for maintaining records of calibration, equipment performance, and any adjustments made, ensuring transparency and accountability in the manufacturing process.
A quality management system is ultimately employed to consolidate all these standards in a single location and gather measurements from machines and metrology teams for comparison against the standards. Having a QMS allows users to swiftly detect deviations from standards and implement corrective actions.
Implementing metrological traceability in a manufacturing environment involves connecting various systems using Quality 4.0 principles. Quality 4.0 integrates traditional quality management practices with advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and big data analytics. This integration allows for real-time monitoring and data analysis, providing insights that can improve manufacturing processes and product quality.

Connecting the QDM Platform with Metrolog and Silma is a practical example of implementing metrological traceability. The QDM Platform enables secure access to quality data from any source, anywhere in the world. By linking it with Metrolog and Silma, manufacturers can view individual measurement sessions, exchange data, and analyze trends. This connectivity ensures that all measurement data is accurate, traceable, and easily accessible, facilitating quick decision-making and problem-solving.
Maintaining metrological traceability presents several challenges, including the need for regular calibration, managing vast amounts of data, and ensuring that all measurement instruments remain accurate over time. Calibration requires specialized knowledge and equipment, and any lapse can lead to inaccurate measurements and compromised product quality.
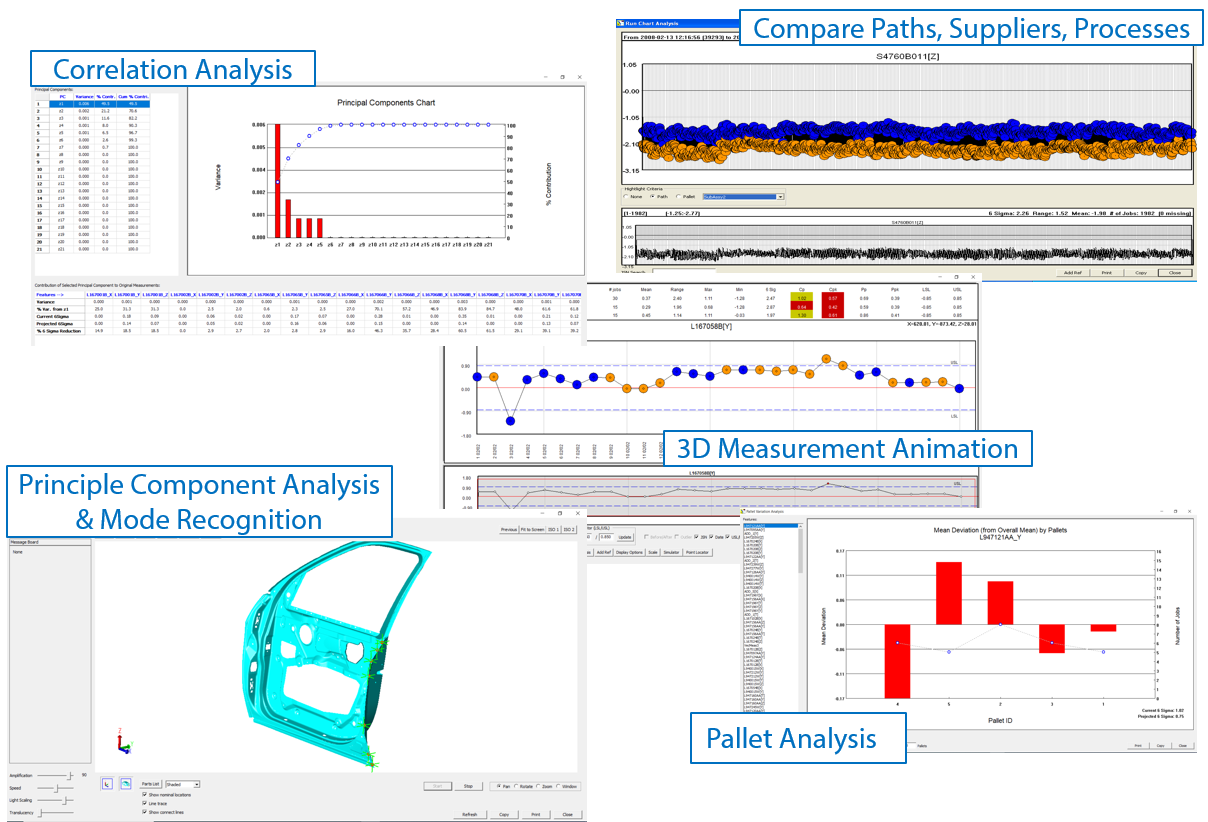
Solutions to these challenges include investing in state-of-the-art calibration equipment, implementing robust data management systems, and training personnel in best practices for measurement and calibration. Utilizing automated systems and software can also streamline the process, reducing the risk of human error and ensuring that all data is accurately recorded and easily accessible.
The future of metrological traceability in manufacturing is likely to be shaped by advancements in technology. The continued development of 5-axis CMMs (Coordinate Measuring Machines) will enhance the precision and efficiency of measurements. These machines can focus on critical-to-quality points, providing highly accurate data that can be shared downstream for analysis and monitoring.
Another trend is the increasing integration of AI and machine learning in metrology. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and trends, helping to pinpoint root causes of manufacturing issues and improve overall quality.
These Stories on 3DCS
No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think