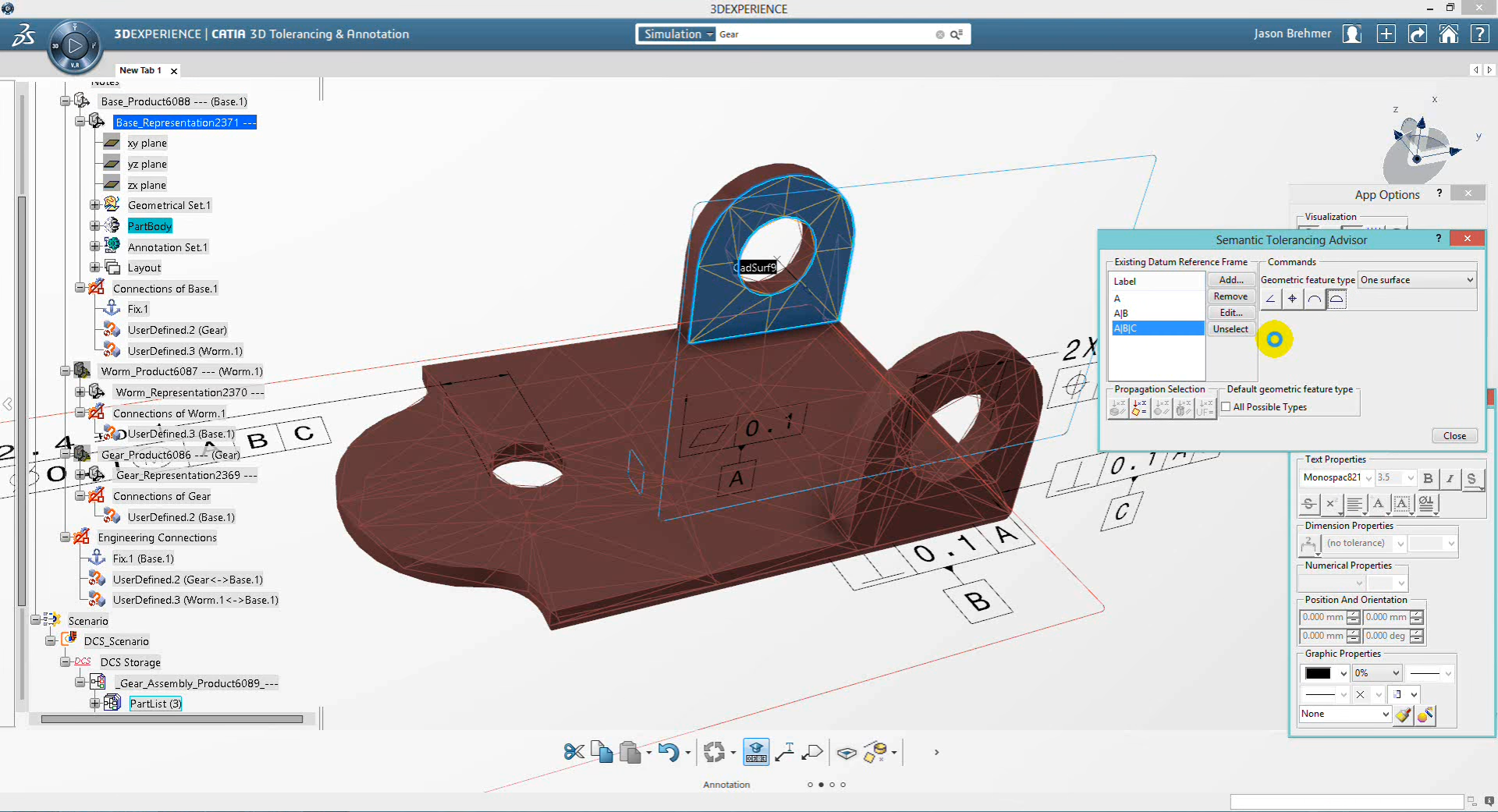
Tolerance analysis is the name given to a number of processes used to determine the overall variation and effect of variation on products stemming from imperfections in manufactured parts.
As part of the tolerance analysis process, both original sources of the
 When manufactured, parts are never made to perfect specifications. Due to variation caused by material characteristics and manufacturing processes, such as stamping and machining, parts are always made larger or smaller than their nominal design. This variation is captured in design as tolerances, depicting the range of variation acceptable in the design.
When manufactured, parts are never made to perfect specifications. Due to variation caused by material characteristics and manufacturing processes, such as stamping and machining, parts are always made larger or smaller than their nominal design. This variation is captured in design as tolerances, depicting the range of variation acceptable in the design.
Tolerancing is the process of determining acceptable upper and lower limits on part dimensions. These dimensions are generally a +/-, which designates how much larger or smaller a given dimension, such as an edge, profile or hole size, can be and still assemble and function properly when incorporated into the larger product. Standardized languages have been created to make it easier to understand tolerancing methods and notes from customers,
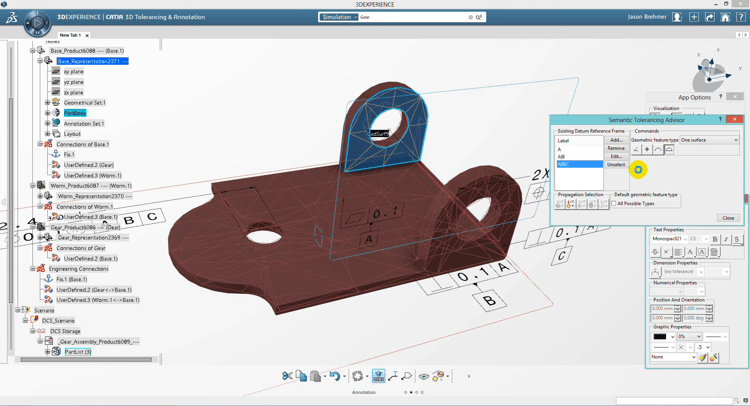
These standard languages include standards like ISO and ASME Y14.5 2009 Standard for the design language of geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T). This standard establishes a uniform practice for stating and interpreting GD&T and related requirements for use on engineering drawings and documents.
GD&T is an important part in determining part tolerances and quality. As stated by ASME,
“GD&T is an essential tool for communicating design intent — that parts from technical drawings have the desired form, fit, function and interchangeability. By providing uniformity in drawing specifications and interpretation, GD&T reduces guesswork throughout the manufacturing process — improving quality, lowering costs, and shortening deliveries.”
Tolerancing directly influences the cost and performance of a product. A piece of sheet metal that is quickly stamped using a stamping die is much cheaper to produce than one that needs to be machined to more precise dimensions.
The same applies for plastics, composites and any given part. The tighter, as in the smaller, the tolerance, the more difficult the part is to produce, and the more expensive the part is. In the same regard, the performance of a part and product is influenced by tolerances. An automobile door will not close well if the tolerances are very large, and may have additional road noise from a poor seal. Aircraft wings may need large amounts of shims if the tolerances are incorrect in order to fit properly to the fuselage. This costs time, money and increases the weight of the aircraft, reducing its fuel efficiency.
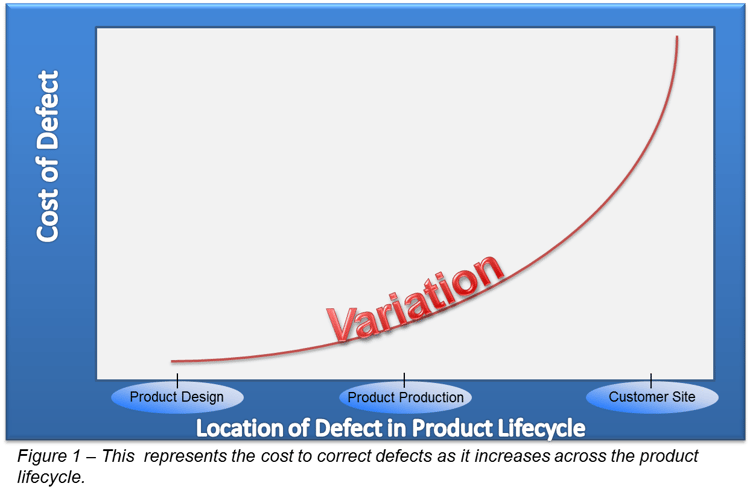
Therefore, tolerancing and tolerance analysis are integral parts of the engineering process and product lifecycle management in order to produce high-quality products at reasonable prices.
Click Here to request a free custom tailored demonstration by a DCS Engineer
These Stories on 3DCS
No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think